December 5th, 2025 marks another World Soil Day but this year, we’re uncovering the hidden intelligence beneath our feet that could revolutionize agriculture forever
World Soil Day 2025: The urgent need for soil memory understanding
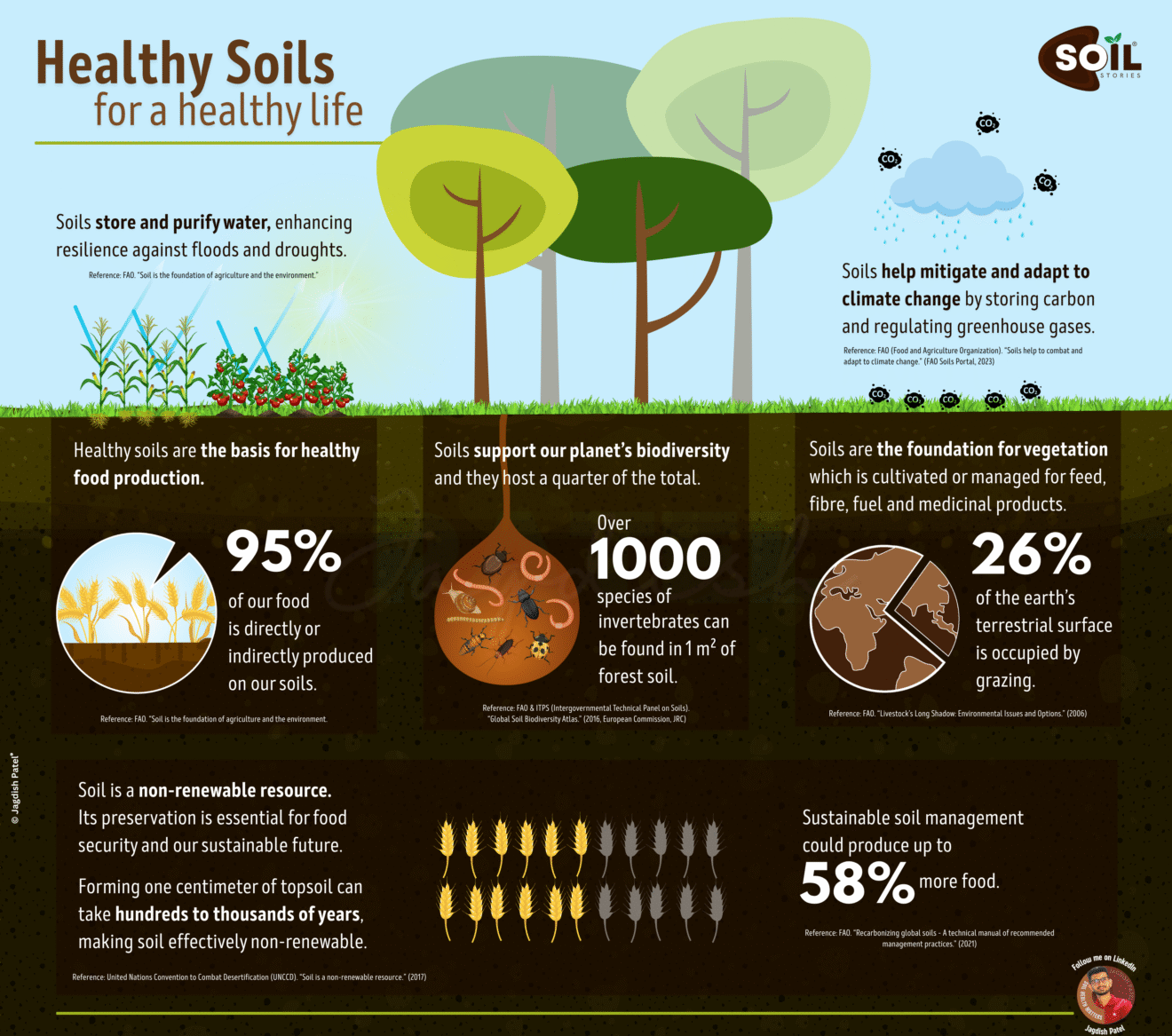
Every December 5th, World Soil Day reminds us that beneath our feet lies one of Earth’s most precious resources. According to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), we lose 24 billion tons of fertile soil annually equivalent to losing 3.2 hectares every second. But what if we told you that your soil is far more intelligent than you ever imagined?
On this World Soil Day 2025, we’re revealing 7 amazing secrets your soil remembers that could completely transform how you approach farming. These aren’t just theories they’re practical realities that forward-thinking farmers are already using to combat the global soil crisis.

This 65 second film reveals what truly happens beneath a field as earthworms, microbes, roots, and nutrients build the living foundation of our food system. It also shows how harvesting, chemicals, and repeated soil disturbance erase that life over time.
Click the thumbnail to watch the full video and see why soil carries a memory of every action we take.
The global soil memory crisis: Shocking statistics
| Critical soil facts (FAO/UN data) | Impact |
|---|---|
| 33% of global soil is already degraded | 1.5 billion people affected |
| 95% of food comes from soil | Direct threat to food security |
| Soil formation: 500-1000 years per inch | Memory loss is nearly permanent |
| Current loss rate: 10-40x faster than formation | Accelerating memory degradation |
| Economic loss: $400 billion annually | Direct cost of soil memory damage |
Source: FAO Global Soil Partnership, UN Convention to Combat Desertification, 2025
Secret #1: Your soil remembers every chemical application
The chemical memory bank
Important note: Chemical inputs aren’t inherently bad they become problematic when used excessively or without understanding soil memory impacts. Balanced, strategic chemical use can support soil health when combined with biological practices.
Your soil doesn’t just process fertilizers and pesticides it remembers them. Research from the International Soil Reference and Information Centre shows that chemical memory can persist for 20-50 years in soil systems.
This chemical memory system explains why some fields require ever-increasing fertilizer rates while others maintain fertility with minimal inputs. Understanding your soil’s chemical history is the first step toward breaking the addiction cycle and rebuilding biological intelligence that naturally manages nutrients.
Chemical memory impact table
| Input type | Memory duration | Measurable effects | Recovery time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic nitrogen | 5-15 years | Reduced microbial diversity | 3-8 years |
| Phosphorus fertilizer | 10-25 years | P-fixation patterns | 5-12 years |
| Herbicides | 1-10 years | Soil biology disruption | 2-7 years |
| Heavy metals | 50-100+ years | Permanent contamination | Often irreversible |
| Organic amendments | 3-20 years | Enhanced biological memory | Immediate benefits |
Memory recovery success story
A University of Wisconsin study tracked two neighboring farms: Chemical-dependent farm: Required 40% more inputs after 20 years Memory-positive farm: 35% reduction in input costs, 25% yield improvement
Soil pollution effects demonstrate how damaged soil memory creates long-term agricultural challenges, especially when chemicals are overused without consideration for biological balance.
Secret #2: Soil memory records your tillage history
Physical memory degradation data
According to FAO’s Global Soil Organic Carbon Map, intensive tillage has caused:
Every time you till, your soil remembers the disruption to its underground architecture. This physical trauma breaks fungal networks, destroys soil aggregates, and triggers carbon loss that can persist for decades. The good news is that soil structure memory can be rebuilt faster than chemical memory through strategic no-till practices combined with diverse cover crops.
Tillage memory impact analysis
| Tillage intensity | Organic matter loss | Microbial decline | Water infiltration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional (2x/year) | 50-70% over 50 years | 60-80% reduction | 75% decrease |
| Reduced (1x/year) | 30-40% over 50 years | 40-50% reduction | 50% decrease |
| No-till | 10-20% initial loss | 20-30% temporary decline | 25% improvement |
| No-till + cover crops | Net gain after year 3 | 150% increase by year 5 | 200% improvement |
The USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service reports that mycorrhizal networks take 3-5 years to rebuild after severe tillage disruption.
Secret #3: Your soil remembers crop rotation patterns
Biological legacy research
European Centre for Environment and Human Health studies show crop rotation memory affects:
Your soil’s microbial community adapts to the root exudates and residues of your chosen crops, creating biological preferences that can last for years. Diverse rotations build rich microbial memory banks, while monocultures create biological amnesia. The difference between a 2-crop rotation and a diverse system can mean the difference between soil degradation and regeneration.
Crop memory benefits matrix
| Rotation type | Soil health score | Yield stability | Input reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn-soy (2-year) | 3.2/10 | 65% | 10% |
| 3-crop + legume | 6.8/10 | 85% | 25% |
| 4+ crops + cover | 8.5/10 | 95% | 40% |
| Diverse perennial | 9.2/10 | 98% | 60% |
Scores based on FAO Soil Health Assessment Protocol, 2025
Research demonstrates that plant microbe partnerships create lasting biological memory that benefits subsequent crops.
Secret #4: Soil memory tracks organic matter management
Carbon memory research data
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2025 report reveals:
Organic matter is your soil’s long-term memory storage system. Each type of organic input creates different memory patterns some providing quick energy bursts, others building stable, decades-long carbon reserves. The key is understanding how to feed your soil’s memory system with the right balance of fresh residues and stable organic compounds that create lasting fertility improvements.
Organic matter memory timeline
| Years | Carbon storage | Microbial diversity | Nutrient cycling | Economic return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | 105-110% baseline | 120-140% baseline | 110-115% baseline | -5 to 5% |
| 3-5 | 125-150% baseline | 150-200% baseline | 130-160% baseline | 15-25% |
| 6-10 | 160-200% baseline | 200-300% baseline | 170-220% baseline | 30-45% |
| 10+ | 200-250% baseline | 300-400% baseline | 250-300% baseline | 45-65% |
Understanding soil organic matter dynamics is crucial for building positive soil memory.
Secret #5: Environmental memory and climate adaptation
Climate memory statistics
UN Environment Programme data shows soil memory’s climate impact:
Your soil remembers every drought, flood, and temperature extreme, building adaptive capacity through biological and physical changes. Soils with rich environmental memory can buffer climate extremes, maintain moisture longer during droughts, and recover faster from flooding. This climate memory becomes increasingly valuable as weather patterns become more unpredictable.
Climate resilience through soil memory
| Memory quality | Drought tolerance | Flood recovery | Temperature buffer | Carbon storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degraded memory | 25% of normal | 2-3 months | ±5°C daily swing | 0.5-1% organic matter |
| Average memory | 60% of normal | 3-6 weeks | ±3°C daily swing | 2-3% organic matter |
| Rich memory | 95% of normal | 1-2 weeks | ±1.5°C daily swing | 4-6% organic matter |
| Optimal memory | 110% of normal | <1 week | ±1°C daily swing | 6-8% organic matter |
Belowground carbon storage systems demonstrate how soil memory contributes to climate solutions.
Secret #6: Soil memory and biological defense systems
Disease suppression research
International Society of Soil Science studies reveal:
Healthy soil remembers past pathogen encounters and builds increasingly sophisticated defense networks. This biological memory system can provide better disease protection than chemical fungicides while simultaneously improving plant nutrition and stress tolerance. The investment in biological defense memory pays dividends for years, creating self-sustaining protection that gets stronger over time.
Biological defense memory effectiveness
| Defense type | Establishment time | Memory duration | Effectiveness rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trichoderma networks | 6-12 months | 5-10 years | 70-90% pathogen suppression |
| Beneficial bacteria | 3-6 months | 3-5 years | 60-80% disease reduction |
| Mycorrhizal defense | 12-18 months | 8-15 years | 80-95% stress tolerance |
| Integrated biological | 18-24 months | 15+ years | 90-98% system resilience |
Trichoderma activity exemplifies how soil memory creates lasting biological protection systems, reducing the need for excessive chemical interventions.
Secret #7: Economic memory of management decisions
Financial impact analysis
World Bank Agricultural Development Report 2025 shows:
Your soil’s economic memory tracks every investment you make, compounding positive management decisions into long-term profitability while penalizing short-term thinking with declining returns. Farmers who understand economic memory invest in practices that build value over time, while those who ignore it find themselves trapped in expensive input cycles with diminishing profits.
Economic returns from soil memory investment
| Management approach | 5-year ROI | 10-year ROI | Risk reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical intensive | 15-25% | 10-20% | Low (high volatility) |
| Conventional + biology | 25-35% | 30-45% | Medium |
| Regenerative transition | 20-30% | 45-65% | Medium-high |
| Memory-optimized system | 35-50% | 65-85% | High (stable yields) |
Implementing soil memory solutions: Action framework
Assessment and monitoring protocol
Soil memory health indicators
| Indicator | Poor memory | Average memory | Excellent memory | Test frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic matter | <2% | 2-4% | >4% | Annual |
| Microbial biomass | <200 μg/g | 200-400 μg/g | >400 μg/g | Biannual |
| Water infiltration | <0.5 in/hr | 0.5-2 in/hr | >2 in/hr | Seasonal |
| Aggregate stability | <40% | 40-70% | >70% | Annual |
| Root penetration | <6 inches | 6-12 inches | >12 inches | Growing season |
Understanding soil microbes and nutrient cycling helps farmers interpret these memory indicators effectively.
World Soil Day 2025: Technology for soil memory
Digital soil memory tools
Modern assessment technologies
| Technology | Memory aspect | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| DNA sequencing | Biological diversity | 95-99% |
| Spectral analysis | Chemical composition | 85-95% |
| Penetrometer | Physical structure | 90-98% |
| Enzyme assays | Biological activity | 80-90% |
| Thermal imaging | Stress patterns | 75-85% |
Your World Soil Day 2025 action plan
Immediate steps (December 2025)
- Soil memory assessment Conduct comprehensive biological and chemical testing Restore soil memory using proven protocols Establish baseline measurements
- Memory-building strategy Design 3-year transition plan Budget for biological inputs Plan diverse crop rotations
Implementation timeline
12-month memory restoration program
| Month | Action | Expected outcome | Investment level |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | Assessment & planning | Clear memory baseline | Low |
| 4-6 | Biological inoculants | Initial microbial establishment | Medium |
| 7-9 | Cover crop establishment | Enhanced biological activity | Medium |
| 10-12 | Monitoring & adjustment | Measurable improvements | Low |
Balanced chemical use in soil memory management
Smart chemical integration
Remember: Chemicals aren’t the enemy excessive use without biological balance is. Modern soil memory management integrates:
Precision application: Using soil memory data to optimize timing and rates Biological buffering: Supporting microbial communities that process chemicals efficiently Reduced dependency: Building soil memory that naturally supplies more nutrients Strategic timing: Applying chemicals when soil biology can best integrate them
The key is working with soil memory rather than against it, using both biological and chemical tools wisely.
Conclusion: Soil memory as agriculture’s future
This World Soil Day 2025, the FAO estimates we have only 60 years of topsoil remaining at current degradation rates. The 7 amazing secrets your soil remembers offer hope but only if we act decisively.
The global stakes: 815 million people face food insecurity (UN World Food Programme) 3.2 billion people live in degraded agricultural areas (UNCCD) $23.7 trillion in ecosystem services depend on healthy soil (OECD). Every management decision creates lasting memory. Choose practices that build biological intelligence, structural resilience, and climate adaptation. Your soil remembers everything make those memories count.
Begin your soil memory journey with assessment, move through strategic planning, and commit to long-term memory-building practices. The future of agriculture depends on farmers who understand and work with soil’s incredible memory systems.
Happy World Soil Day 2025 transform farming through soil memory wisdom.
Key resources:
FAO Global Soil Partnership Official soil health data and protocols
UN Sustainable Development Goals Land degradation neutrality targets
IPCC Climate and Land Report Soil carbon and climate research
World Bank Agricultural Statistics Economic impact data