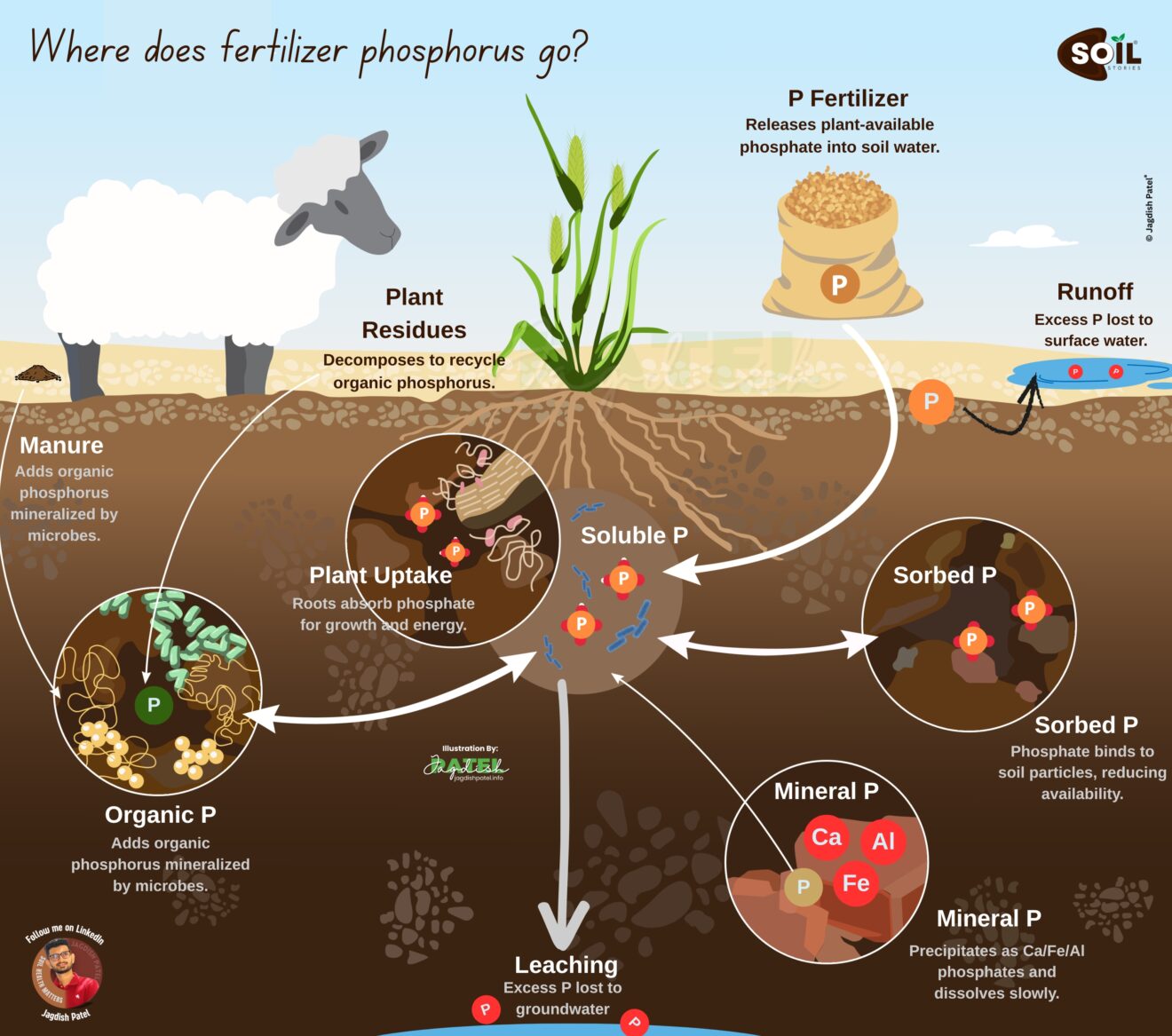
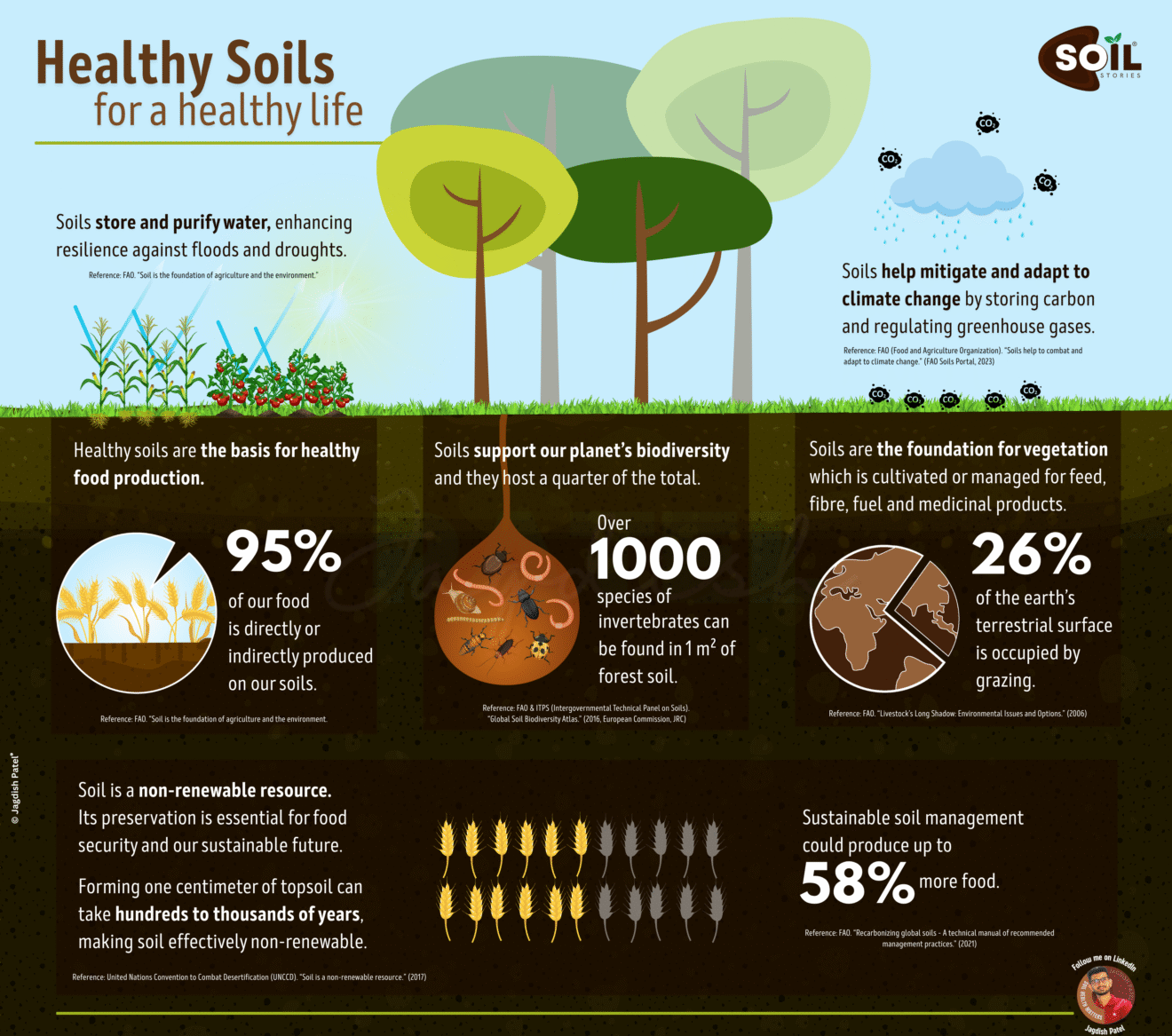
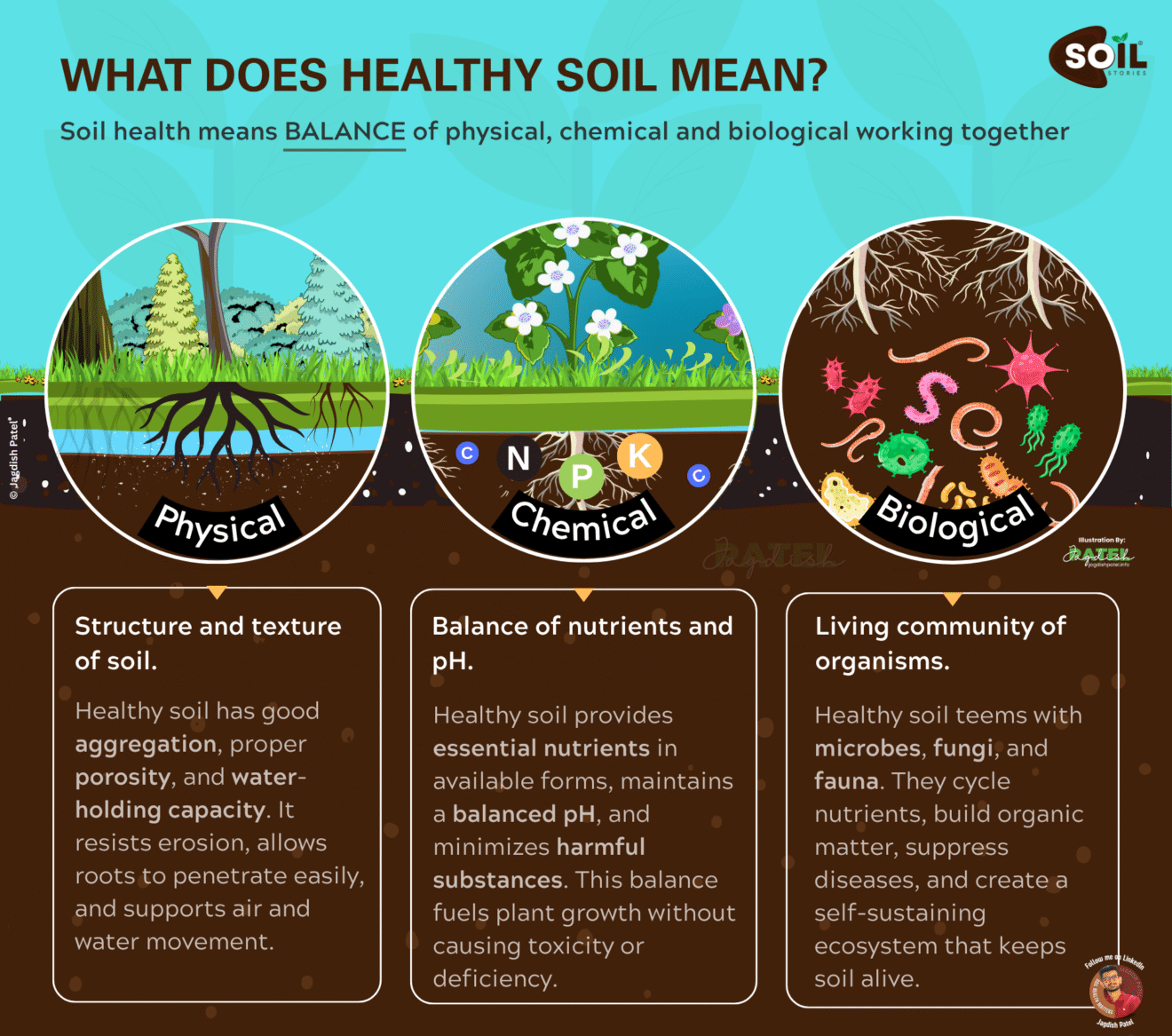
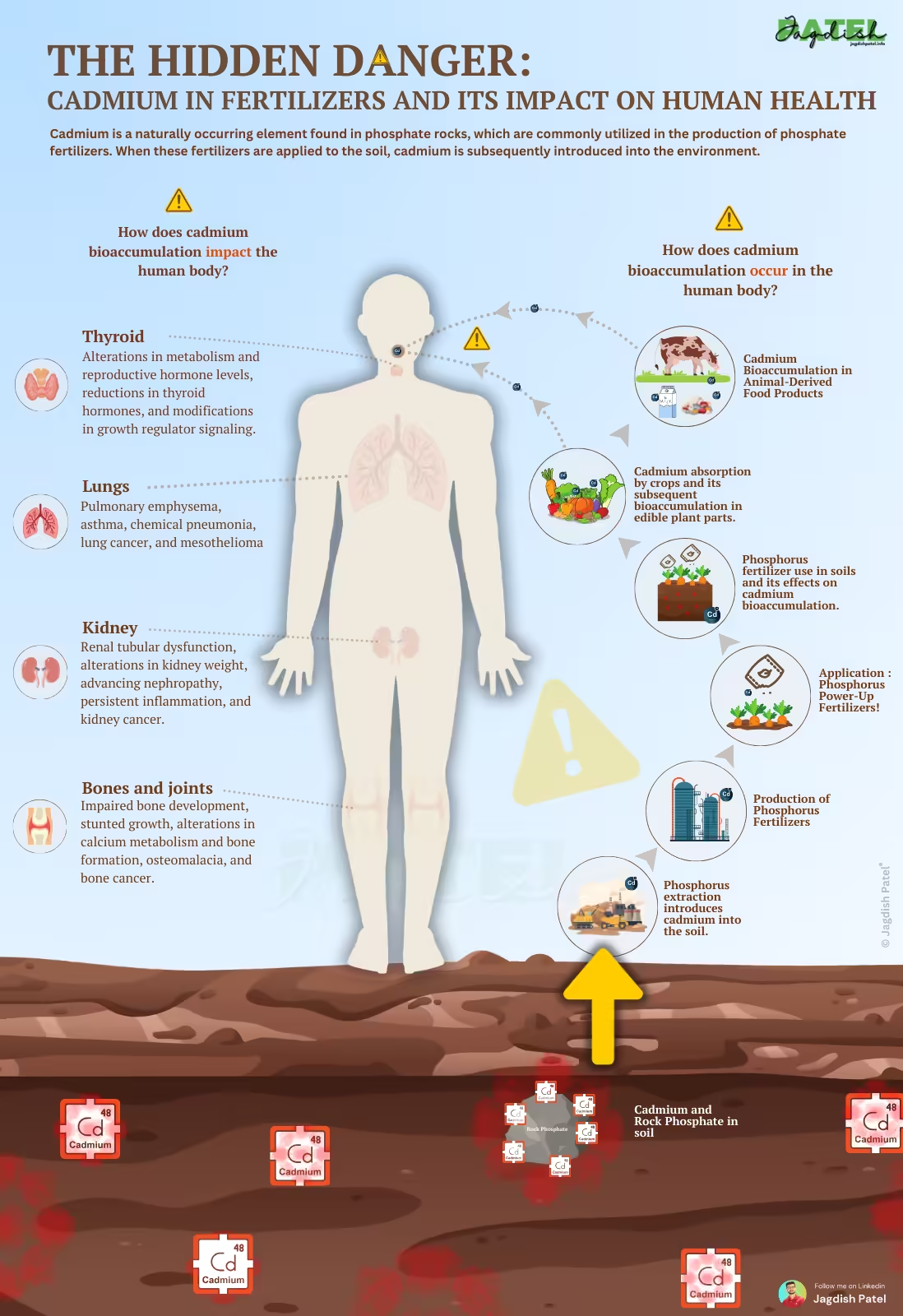
We often hear that in order to lead a healthy life, one needs to consume fresh fruits and vegetables. However, what if these very food have an underlying threat? It is a Shocking revelation but we need to deal with. Cadmium, an incredibly toxic elemental metal, can be found within human food through the fertilizers which aid in increasing agricultural productivity, on the surface seems benign.
This is the crux of suffering the most infuriating dilemma. We use fertilizers to feed the ever-increasing population. Unfortunately, these same fertilizers are able to bring undesirable pollutants to our food systems. Phosphate fertilizers, which are important for plant growth, are obtained from rock phosphates, which normally has cadmium inside it. Repeated applications of this cadmium phosphate in the field will lead to a build up of these cadmium phosphates in the soil. Eventually, they are taken up by crops and find their way into people’s food.
A Global Shadow: Cadmium’s Reach Extends More Faces Than One 🌎
This is not just a problem for one country; it is a global problem. Studies have confirmed the presence of cadmium contamination from fertilizers in a number of countries such as the us, Australia and India and others.
In the US: In its research, the USGS found cadmium in certain phosphate fertilizers at an astonishing 100 mg Cd per kg phosphorus, thereby increasing the risks associated with high concentration phosphate fertilizers. This also results in more and more of this poisonous metal being washed into the ground with each successive application.
Australia These factors pose a great health risk as research has showed that cadmium has being found to be increasingly concentrated in agricultural soils over the years as a result of fertilizer application.
India: With its large agricultural sector, there is also a high reliance on phosphate fertilizers which unfortunately means that cadmium contamination is also a factor that the country has to deal with.
Cadmium’s Insidious Danger To Human Health
- There are toxins that our bodies have cleansing functions for, and therefore there is no need for leisurely bid farewell to cadmium. It is an unwelcome guest who takes that type of approach.
- Thyroid : Cadmium can also impair the synthesis of thyroid hormone due to its ability to stimulate the metabolism of this hormone rendering its level low and affecting growth processes.
- Lung : Inhaled cadmium results in thickening of lung tissues and the formation of scars within the lungs which expose one to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, emphysema, and many others.
- Kidney : It is substantiate that the kidneys are the most exquisitely affected by Cadmium toxicity. This has been established to lead to damages in the kidneys, inflammatory disorders, and in the worst case kidney failure, etc additional time.
- Bone : Cadmium disrupts calcium intake and bone mineralization and resorption and hence decreases bone mass, promotes fracture incidence, and induces diseases of bone such as osteoporosis and osteomalacia.
Delving Deeper: The Science Behind the Threat 🔬
Cadmium toxicity, which is indelibly memorable, is linked to diminished levels of CDK1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 1) and cyclin B, as reported in a prominent journal. A recent publication in Environmental Health Perspectives indicates that cadmium, a toxic metal, adversely affected the health of over 14,000 individuals in the United States. A recent study published in The Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology demonstrated that low cadmium levels elevate the risk of various bone fractures, particularly at the radius. These observations present a bleak prognosis for the future health of American society, as numerous food items remain contaminated with cadmium.
Taking Initiative: We can do something about it. 💪
- Cadmium contamination is very hazardous, but we are not hopeless in the battle against this menace. Some measures that can be applied in order to reduce the threat of cadmium contamination include the following:
- Tougher Legislation: There should be more limits in the amount of cadmium present in fertilizers than it currently is. Governments need to define and enforce these measures as to prevent the agricultural fertilizers from becoming an agent of health hazards.
- Monitoring of Soil: It will be important to carry out regular soil analysis to check for cadmium levels and other pollutants on different areas. This makes it possible to implement timely actions and measures.
- Research Into Better Methods: Investigating and advocating the use of low cadmium fertilizers or requiring the use of biofertilisers and natural fertilizers can help to limit the chance of pollution.
- Raising Awareness: Last, but not the least, it is very important to make the farmers, consumers and decision makers engage in the problem of cadmium in fertilizers. People need to be educated as to where the contamination comes from, the health risks associated with it and the measures which can be taken toward these risks.
Conclusion
- Cadmium contamination in fertilizers is a serious issue, but it’s not insurmountable. By taking proactive steps, we can protect our health and safeguard the environment. Remember, sustainable agriculture isn’t just about increasing yields; it’s about ensuring the safety and well-being of both people and the planet.
- Let’s work together to create a healthier, more sustainable future for generations to come. 🤝🌱
References:
- Cadmium in Phosphate Fertilizers: A Growing Concern. Environmental Science & Technology. [Link to journal article]
- Assessing the Health Risks of Cadmium Exposure Through the Food Chain. Journal of Environmental Health. [Link to journal article]
- Cadmium Accumulation in Agricultural Soils: A Global Perspective. Soil Science Society of America Journal. [Link to journal article]
- Impact of Cadmium on Thyroid Function and Hormone Regulation. Endocrine Reviews. [Link to journal article]
- Cadmium Toxicity and Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. [Link to journal article]
- The Role of Cadmium in Bone Loss and Osteoporosis. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. [Link to journal article]
- Cadmium Exposure and Respiratory Health: A Meta-Analysis. Environmental Health Perspectives. [Link to journal article]