What does healthy soil mean for your garden’s success? If you’ve ever wondered why some plants thrive while others struggle, the answer lies hidden beneath the surface. Healthy soil is the foundation of all successful agriculture and gardening, a complex living ecosystem that determines whether your plants will flourish or fail.
Understanding healthy soil isn’t just about dirt; it’s about mastering the intricate balance of physical structure, chemical composition, and biological activity that creates the perfect growing environment.
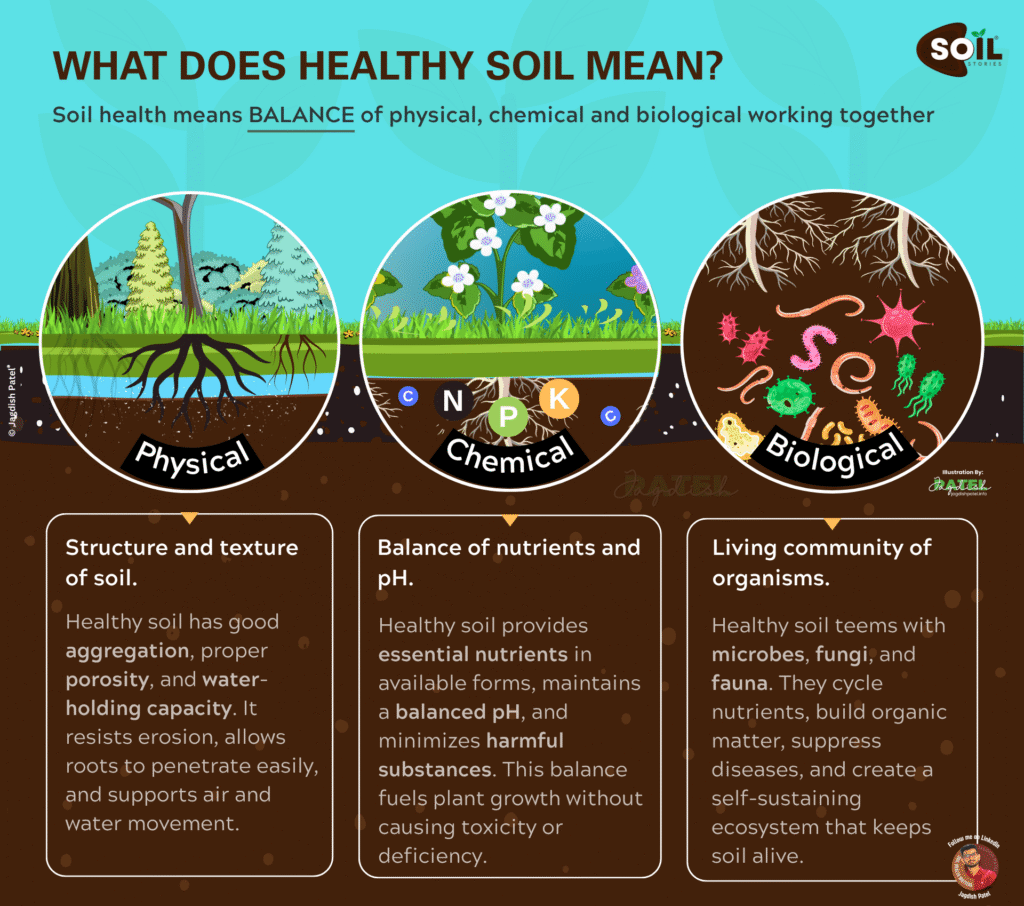
What Does Healthy Soil Really Mean? The Definition That Changes Everything
Healthy soil means achieving the optimal balance of three critical components working in perfect harmony:
- Physical Properties – Structure and texture
- Chemical Properties – Nutrients and pH balance
- Biological Properties – Living organisms and organic matter
This trifecta creates an environment where plants can access nutrients efficiently, roots can penetrate easily, and beneficial microorganisms thrive to support plant health naturally.
The Physical Foundation: Why Soil Structure Matters
Understanding Healthy Soil’s Physical Properties
The physical aspect of what healthy soil means focuses on structure, porosity, and mechanical properties that create the perfect growing environment.
Key Physical Characteristics of Healthy Soil:
- Proper Aggregation
- Well-formed soil particles cluster together
- Creates stable soil structure resistant to erosion
- Prevents harmful compaction
- Optimal Porosity (45-55% pore space)
- Balanced macro and micro pores
- Allows proper air circulation to roots
- Enables efficient water movement and storage
- Water-Holding Capacity
- Retains moisture during dry periods
- Prevents waterlogging during heavy rains
- Supports consistent plant hydration
- Root Penetration Ability
- Loose enough for easy root expansion
- Firm enough to provide plant support
- Allows deep root development for nutrient access
Physical Benefits That Transform Your Garden:
| Physical Property | Garden Benefit | Impact on Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Good Aggregation | Erosion resistance | Stronger root systems |
| Proper Porosity | Better drainage | Reduced root rot |
| Water Retention | Drought tolerance | Consistent growth |
| Easy Penetration | Deep rooting | Enhanced nutrient uptake |
The Chemical Balance: Unlocking Nutrient Secrets
What Healthy Soil Means Chemically
The chemical component of healthy soil focuses on nutrient availability, pH optimization, and the absence of toxic substances that could harm plant growth.
Essential Chemical Properties for Healthy Soil:
- Complete Nutrient Availability
- Primary nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K)
- Secondary nutrients: Calcium, Magnesium, Sulfur
- Micronutrients: Iron, Zinc, Manganese, Boron, and others
- Nutrients in forms plants can readily absorb
- Optimal pH Balance (6.0-7.5)
- Affects nutrient availability dramatically
- Influences beneficial microbial activity
- Impacts plant root health and function
- High Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
- Soil’s ability to hold and exchange nutrients
- Higher CEC = better nutrient retention
- Reduces expensive fertilizer losses
- Minimal Toxins
- Low levels of heavy metals
- Reduced salt accumulation
- No harmful chemical residues
Chemical Indicators of Truly Healthy Soil:
- Balanced nutrient ratios without deficiencies or toxicities
- Stable pH levels requiring minimal amendments
- High organic matter content (3-6% in most soils)
- Excellent nutrient retention reducing fertilizer needs by 30-50%
The Biological Revolution: Living Soil Ecosystem
The Underground Metropolis That Defines Healthy Soil
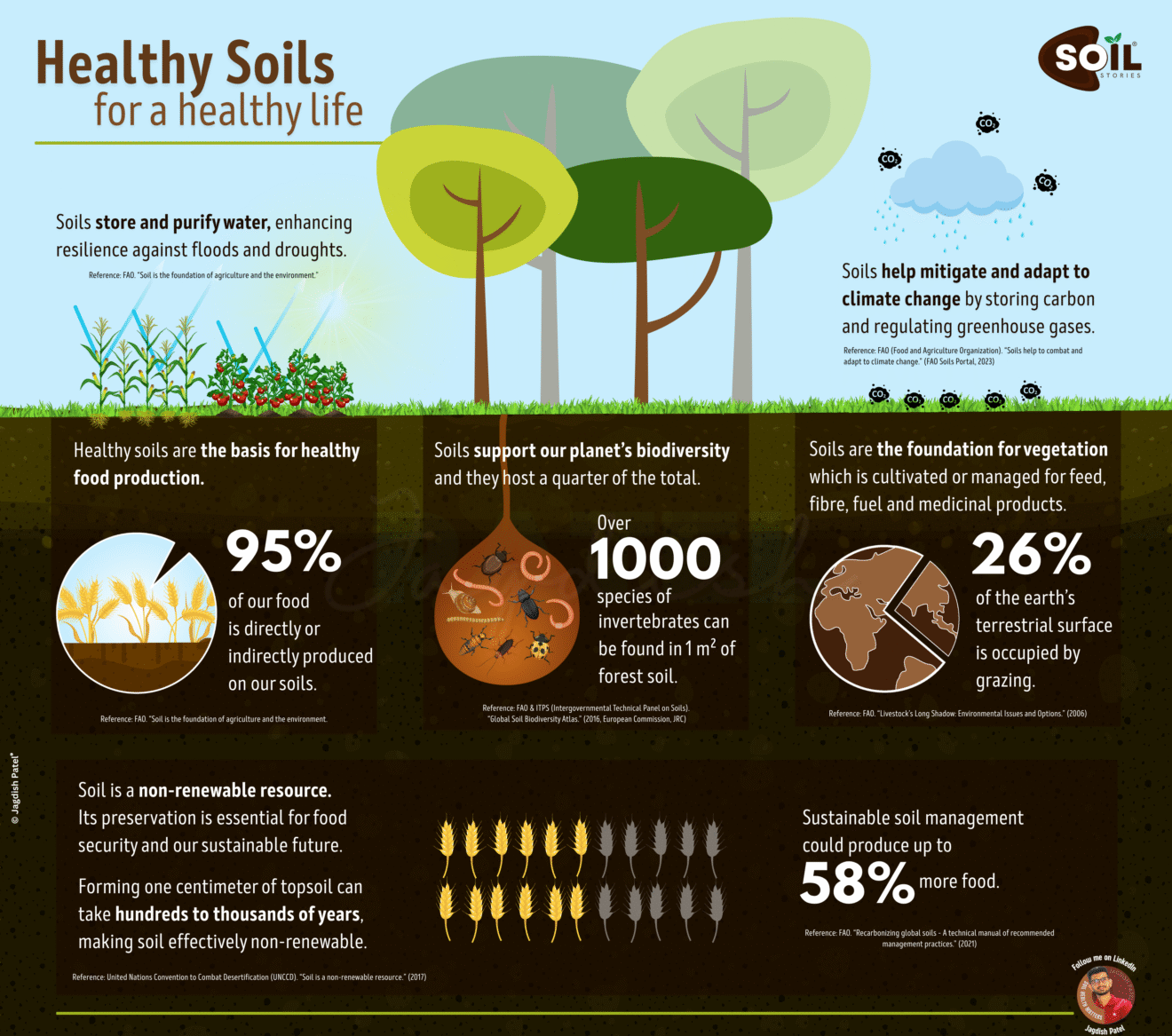
Understanding what healthy soil means biologically reveals nature’s most incredible secret: healthy soil contains 1 billion living organisms per gram – creating one of Earth’s most diverse ecosystems beneath your feet.
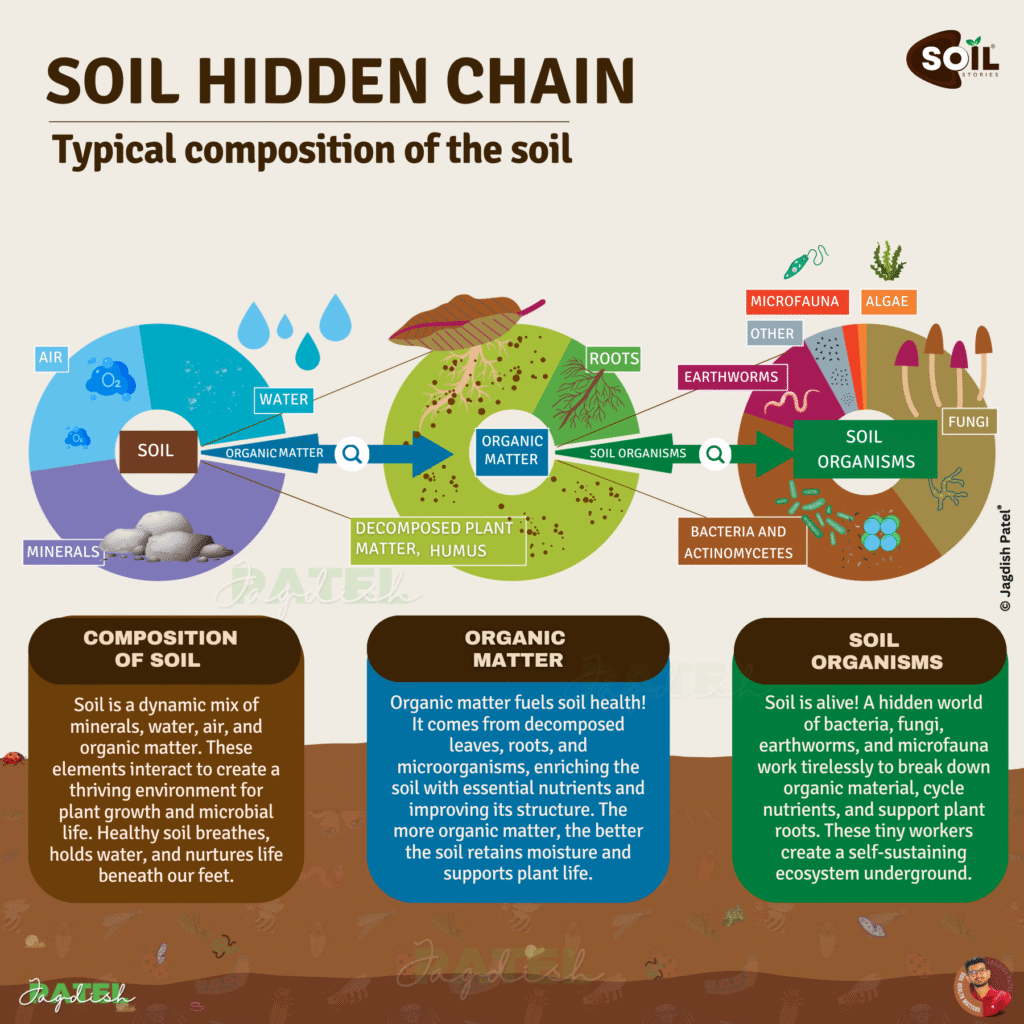
The Biological Powerhouses:
- Soil Microbes (The Nutrient Factories)
- Bacteria: 100 million to 1 billion per gram
- Break down organic matter into plant food
- Fix atmospheric nitrogen naturally
- Suppress plant diseases effectively
- Fungi and Mycorrhizae (The Internet of Plants)
- Form symbiotic relationships with 90% of plants
- Extend root systems up to 1000 times
- Transport nutrients and water efficiently
- Create strong soil aggregation
- Soil Fauna (The Ecosystem Engineers)
- Earthworms: nature’s soil aerators and fertilizer producers
- Arthropods: break down organic matter rapidly
- Protozoa: release plant-available nutrients
- Nematodes: cycle nutrients and control harmful pests
- Organic Matter (The Foundation)
- Provides essential food for soil organisms
- Improves soil structure dramatically
- Stores carbon and nutrients long-term
- Increases water retention by 20-30%
Biological Benefits That Create Garden Magic:
- Natural pest and disease control (reducing pesticide needs by 60%)
- Improved nutrient cycling and availability
- Enhanced soil structure formation
- Increased carbon sequestration
- Better plant stress tolerance during droughts and heat
The Synergy Secret: How All Components Work Together
Why Healthy Soil Means Perfect Integration
What healthy soil truly means isn’t just having good physical, chemical, OR biological properties – it’s achieving perfect synergy between all three components:
The Powerful Connections:
Physical + Chemical Synergy:
- Good structure allows better nutrient movement
- Proper pH enhances structural stability
- Adequate porosity improves chemical reactions
Chemical + Biological Synergy:
- Balanced nutrients support diverse microbial communities
- Microbes make nutrients 3x more available to plants
- Biological activity naturally buffers pH changes
Biological + Physical Synergy:
- Soil organisms create superior soil aggregation
- Root systems improve soil structure naturally
- Organic matter enhances water-holding capacity by 25%
Why Healthy Soil Matters: The Global Impact
Environmental Benefits of Understanding What Healthy Soil Means
- Climate Change Fighter
- Healthy soils store 2.5 times more carbon than the atmosphere
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly
- Improve climate resilience for communities
- Water Quality Guardian
- Filter 99% of pollutants before reaching groundwater
- Reduce agricultural runoff by 40%
- Prevent costly soil erosion and sedimentation
- Biodiversity Protector
- Support 25% of Earth’s total biodiversity
- Provide habitat for countless beneficial species
- Maintain critical ecosystem balance
Economic Benefits That Impact Your Wallet:
| Benefit | Savings/Gains | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Yields | 20-40% higher | 2-3 years |
| Reduced Fertilizer | 30-50% savings | 1-2 years |
| Lower Pest Control | 60% reduction | 1 year |
| Water Efficiency | 25% less irrigation | Immediate |
7 Proven Strategies to Build Healthy Soil
Practical Steps to Achieve What Healthy Soil Means
1. Increase Organic Matter (The Foundation)
- Add 2-4 inches of quality compost annually
- Use diverse cover crops year-round
- Minimize tillage to preserve soil structure
- Return crop residues to feed soil organisms
2. Protect Soil Biology (The Life Force)
- Reduce chemical inputs when possible
- Avoid soil compaction from heavy equipment
- Maintain consistent soil moisture levels
- Provide diverse food sources for beneficial microbes
3. Monitor Soil Health Regularly
- Conduct comprehensive soil tests annually
- Perform visual soil assessments monthly
- Track organic matter levels over time
- Monitor beneficial biological activity indicators
4. Implement Regenerative Practices
- Practice diverse crop rotation systems
- Use integrated pest management approaches
- Apply conservation tillage methods
- Utilize precision agriculture techniques
5. Feed the Soil Food Web
- Apply mycorrhizal inoculants to new plantings
- Use compost teas to boost microbial populations
- Add beneficial bacterial supplements
- Incorporate fermented plant extracts
6. Optimize Water Management
- Install efficient irrigation systems
- Use mulching to retain soil moisture
- Create proper drainage for excess water
- Implement rainwater harvesting systems
7. Balance Soil Chemistry Naturally
- Use organic amendments instead of synthetic fertilizers
- Apply lime or sulfur to adjust pH naturally
- Add rock dust for slow-release minerals
- Incorporate green manures for nitrogen fixation
Testing Your Soil Health: Know What You’re Working With
Key Indicators to Monitor for Healthy Soil
Physical Health Tests:
- Jar Test – Assess soil texture composition
- Penetration Test – Check for compaction issues
- Water Infiltration – Measure drainage capacity
- Aggregate Stability – Test soil structure strength
Chemical Health Tests:
- pH Levels – Optimal range 6.0-7.5
- Nutrient Content – NPK and micronutrient analysis
- Organic Matter Percentage – Target 3-6%
- Cation Exchange Capacity – Nutrient holding ability
Biological Health Tests:
- Earthworm Count – 10+ per cubic foot indicates health
- Microbial Biomass – Total living organisms
- Soil Respiration – Biological activity measurement
- Enzyme Activity – Nutrient cycling efficiency
The Future of Healthy Soil: Revolutionary Advances
Emerging Technologies Transforming What Healthy Soil Means
Current Innovations:
- Precision soil mapping for targeted management
- Biological soil amendments for enhanced microbial activity
- Smart sensors for real-time soil monitoring
- AI-powered recommendations for optimal soil management
Global Initiatives: The 4 per 1000 Initiative aims to increase global soil organic matter by 0.4% annually, demonstrating worldwide recognition of soil health’s critical importance.
Common Mistakes That Destroy Healthy Soil
What NOT to Do When Building Soil Health
- Over-tilling – Destroys soil structure and kills beneficial organisms
- Chemical overuse – Disrupts natural biological balance
- Ignoring pH – Limits nutrient availability severely
- Compaction – Restricts root growth and water movement
- Removing organic matter – Starves soil organisms
- Monocropping – Depletes specific nutrients and reduces biodiversity
Conclusion: Transform Your Growing Success Today
Understanding what healthy soil means is the difference between gardening frustration and incredible success. Healthy soil creates the perfect balance of physical structure, chemical availability, and biological activity that transforms ordinary gardens into thriving ecosystems.
This living system beneath your feet represents one of nature’s most valuable assets, worth an estimated $30 trillion globally in ecosystem services. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you’re not just improving your garden; you’re contributing to climate stability, water conservation, and biodiversity protection.
Take action today:
- Test your soil to understand current conditions
- Start adding organic matter immediately
- Protect and nurture soil biology
- Monitor progress with regular assessments
Whether you’re managing acres of farmland or a small backyard garden, investing in soil health delivers incredible returns in plant performance, environmental benefits, and long-term sustainability.
Remember: healthy soil isn’t just the foundation of successful growing – it’s the key to a healthier planet.
External Resources: