The Carbon Cycle: A Delicate Balance
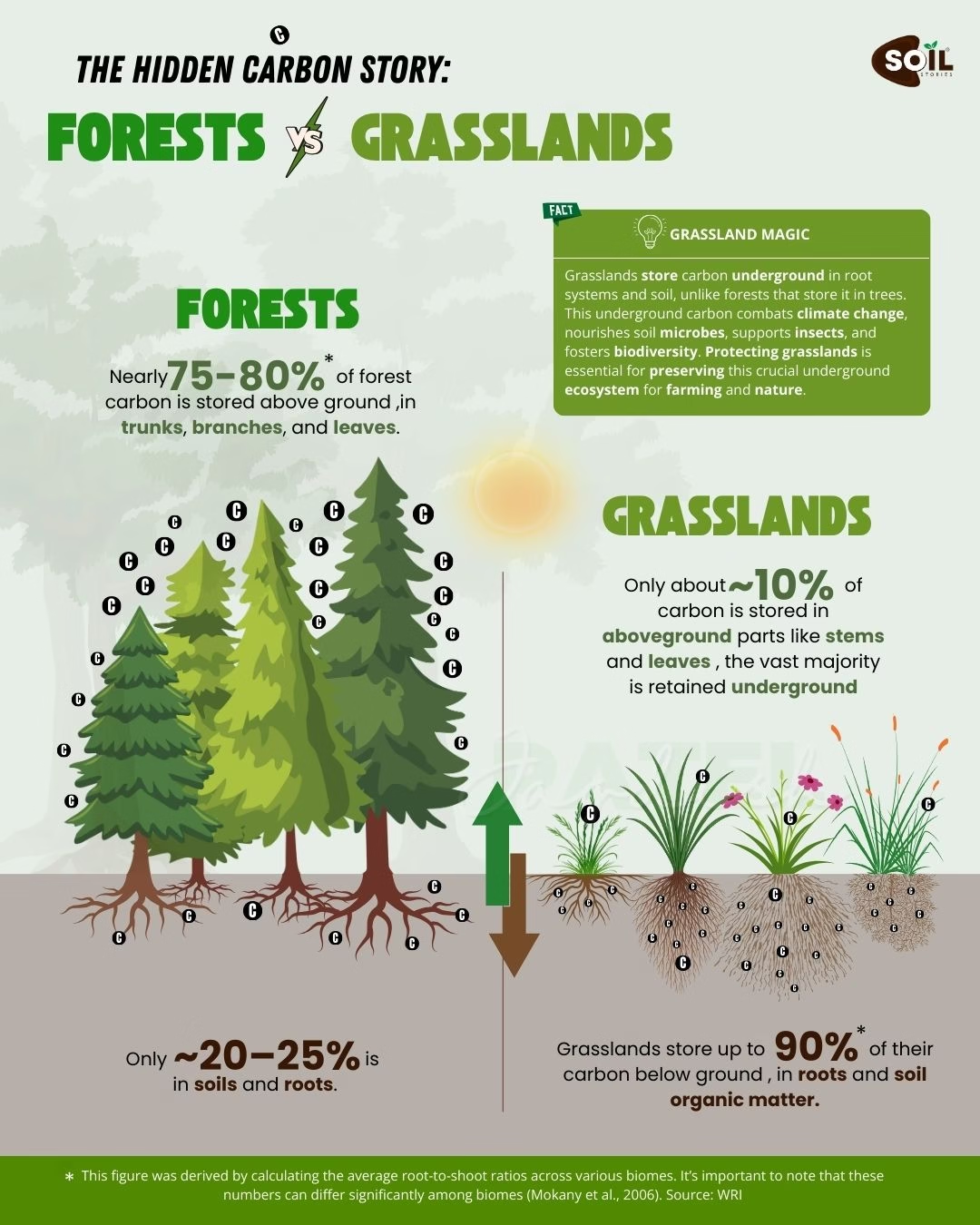
The carbon cycle is a complex system where carbon moves between the atmosphere, plants, animals, and the soil. In agriculture, this cycle is particularly important because healthy soil acts as a significant carbon sink, meaning it can store vast amounts of carbon, helping to mitigate climate change.
I’ve always found the intricate dance of life beneath our feet to be fascinating as a former soil scientist turned illustrator. Soil, often overlooked and undervalued, is a dynamic ecosystem teeming with activity. It’s not just dirt; it’s a living, breathing entity that plays a crucial role in the health of our planet. Today, I want to shed light on one of the most vital processes happening in the soil: the carbon cycle.
Photosynthesis: The Engine of Life
The process begins with photosynthesis. Plants, using sunlight as energy, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter, such as leaves, stems, and roots. This organic matter eventually becomes part of the soil when plants die or shed their leaves.
Soil as a Carbon Reservoir
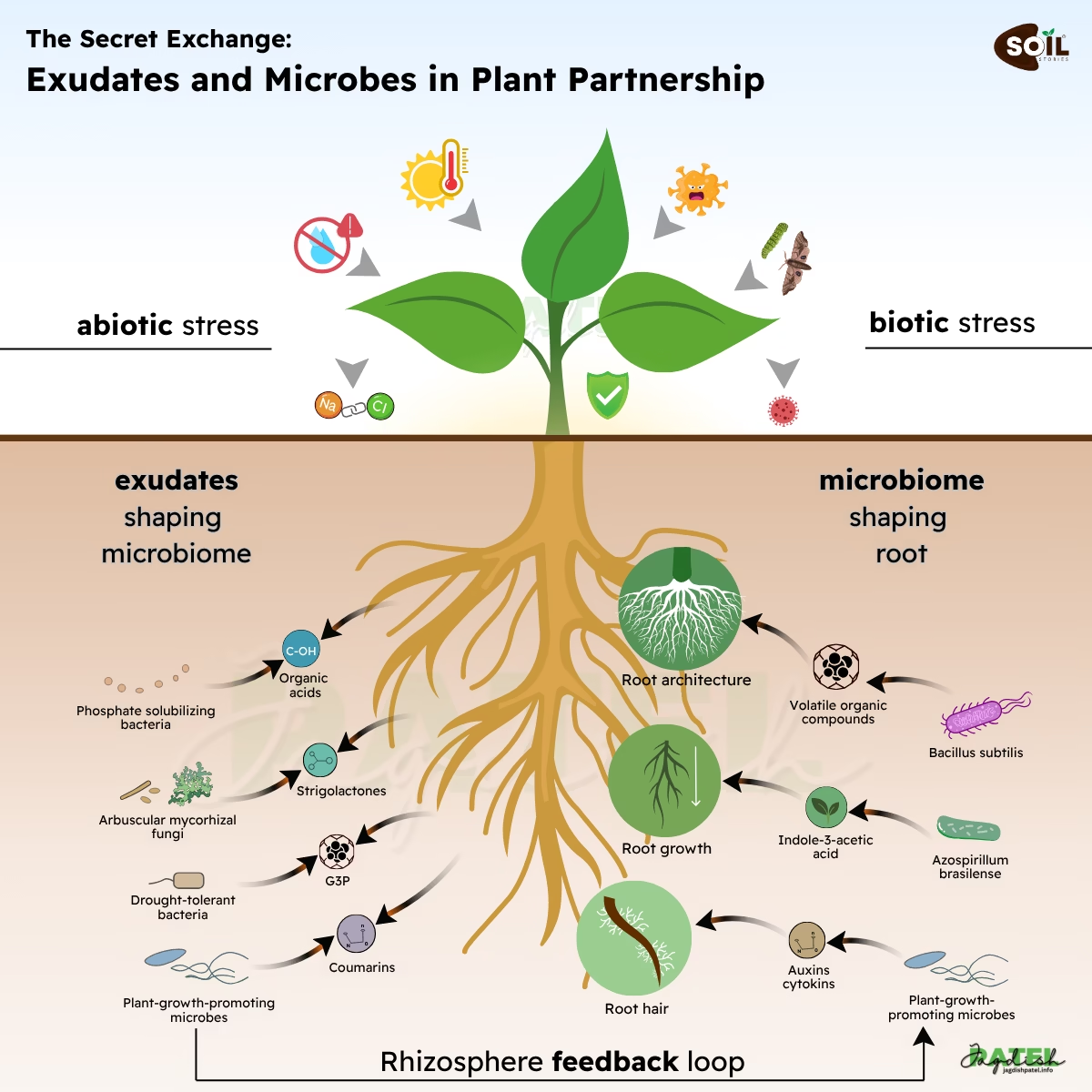
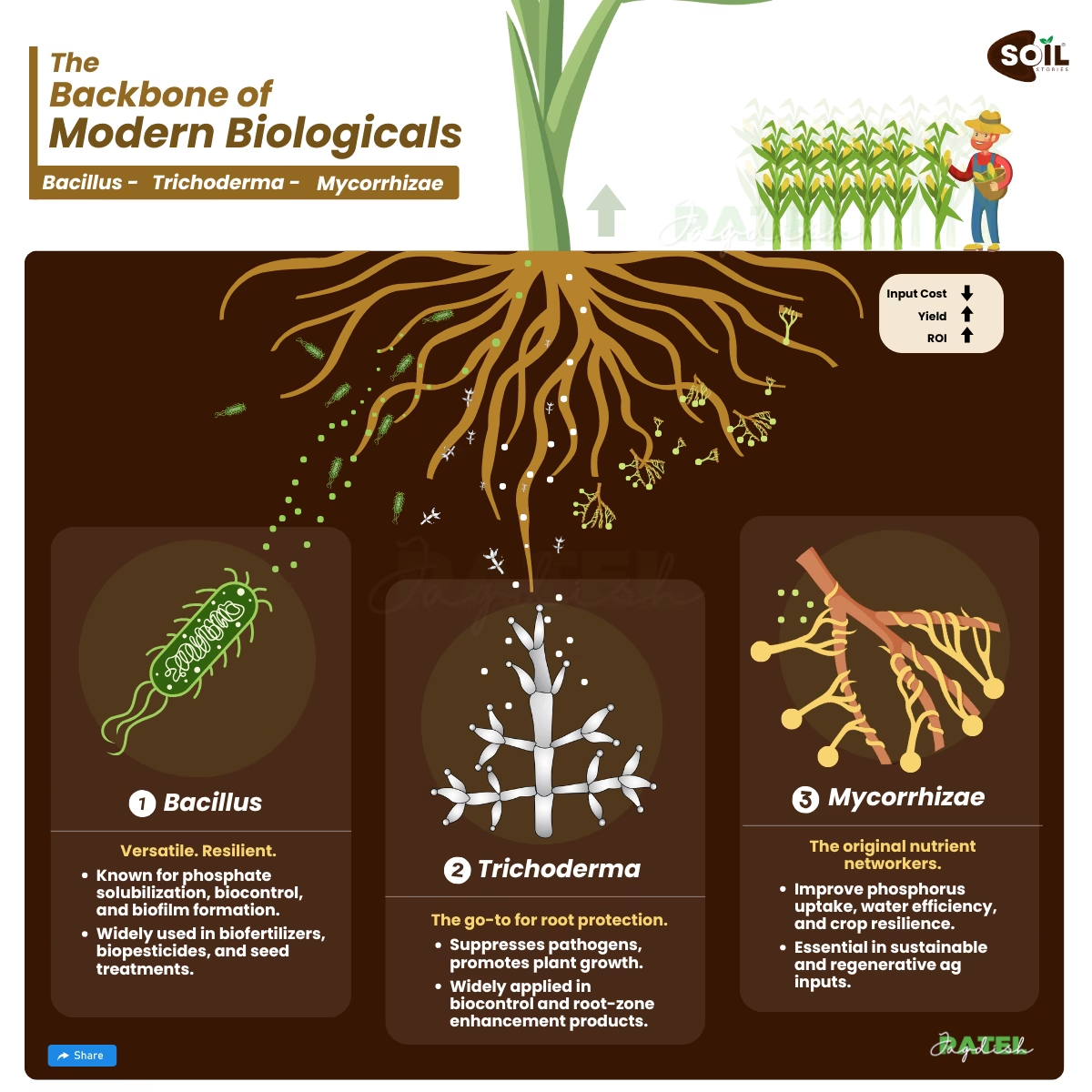
After it has been introduced into the soil, microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi begin to decompose organic waste. A portion of the carbon that is stored in the soil as stable organic matter is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide throughout the process of decomposition; nevertheless, a large portion of the carbon is retained in the soil. This is when the true value of healthy soil is revealed. Through the implementation of techniques such as cover cropping, no-till farming, and crop rotation, the capacity of soil to store carbon can be improved, so transforming agriculture into a potent weapon in the fight against climate change.
An Imminent Danger of Disruption
We regret to inform you that agricultural methods that are not sustainable, such as intensive tilling and excessive fertilizer use, have the potential to disrupt the carbon cycle. These practices can result in the degradation of soil, which in turn reduces the soil’s capacity to store carbon and even releases carbon that has been stored back into the atmosphere, which exacerbates the problem of climate change.
For the sake of our future, we are tending to the soil.
In our capacity as stewards of the land, it is our responsibility to protect and cultivate the soil in order to maintain its state of health. There are a number of potential outcomes that could result from the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices. These outcomes include improving the health of the soil, increasing the amount of carbon that is sequestered, and establishing an agricultural system that is more robust and productive. There is a situation that is beneficial to both the farmers and the environment at the same time. This is a setting that is advantageous.
The Value of Visual Representation
In my capacity as an illustrator, I am of the opinion that art possesses the capability of conveying intricate scientific ideas in a manner that strikes a chord with individuals. By means of my illustrations, I endeavor to convey the splendor and intricacy of the ecosystem that exists inside the soil, with the goal of motivating others to recognize the significance of this ecosystem and to take measures to preserve it.
It is important to keep in mind that good soil is the basis for a healthy planet. It is imperative that we collaborate in order to cultivate the soil and establish a future that is sustainable for future generations.
Soil Erosion: The Silent Thief Stealing Our Future